Delivery Variance
Introduction/Purpose:
The Delivery Variance Master serves as a centralized repository for managing delivery variance data within the transporter system. It plays a crucial role in tracking and overseeing potential variances that may occur during the delivery process, such as differences in cargo weight, product volume, or delivery time.
These variances are expressed as percentages or specific values and indicate the expected range of deviation (+/-) for particular products or cargo. By setting these variance limits, the system can account for potential discrepancies, aiding in realistic expectations and planning.
Defining delivery variances supports more accurate reporting, decision-making, and overall transport operations. This process ensures that deviations are monitored effectively, contributing to the efficiency and reliability of logistics management.
Dependency :
The Delivery Variance Master has critical dependencies within a transport system. Here are the key dependencies:
- Product Master: The product data used in defining delivery variances must be chosen from the existing Product Master. This ensures that the variances are associated with accurate and standardized product details.
How To Navigate To Delivery Variance Master:
The navigation includes the following steps for viewing the delivery variance masters in the transporter management system
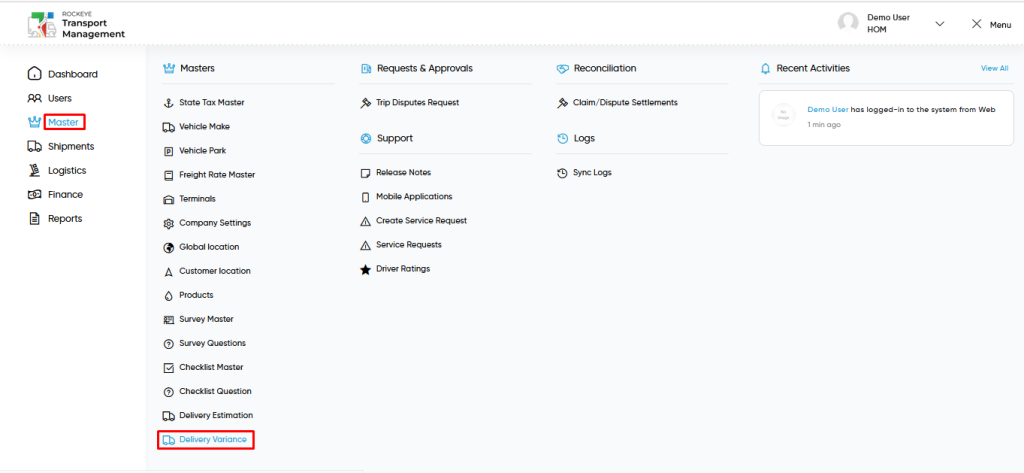
- Click on the Master tab: The master can be accessed by clicking on the Master tab on the side menu.
- Click on delivery variance master: The delivery variance master can be accessed by clicking it from the master section.
Delivery Variance Master Tab Listing:
A delivery variance master listing in a transporter management system is a feature that provides a list of all delivery variances.
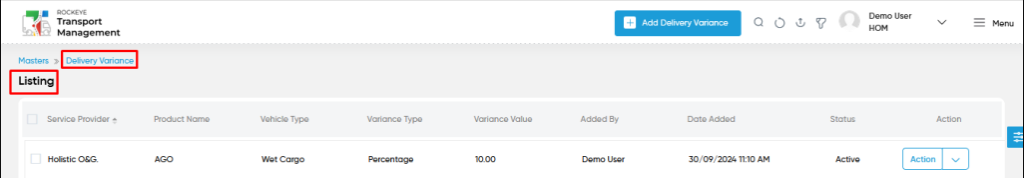
- Users can view the following information in the delivery variance master listing page
- Service Provider
- Product Name
- Vehicle Type
- Variance Value
- Added by and Date Added
- Action to edit or delete
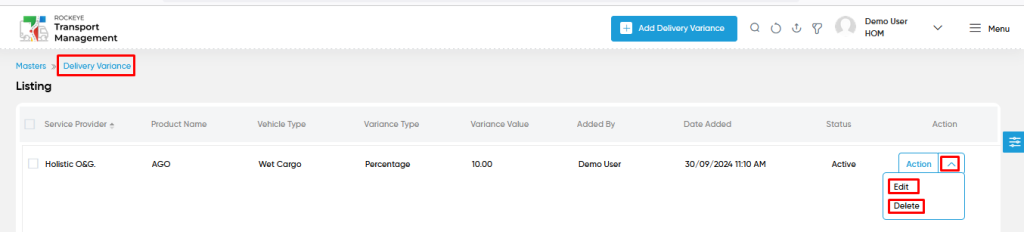
- Users will be able to edit or delete from the action column as shown in below screen.
Delivery Variance – Add Form :
Add new: The “Add new” function allows you to create and add new delivery variance to the system.
- Service Provider : This is specifying the service provider for the delivery variance.
- Vehicle Type : This is specifying to choose the vehicle type (wet / dry / bulk / container ) of the delivery estimation using the dropdown list.
- Product Name : This is specifying the product name of the delivery variance.
- Variance Type : This is specifying to select the variance type as flat or percentage.
- Value : This is specifying the value of the delivery variance.
- Status : This is specifying to choose the status of the delivery variance (active / inactive).
User can perform the following actions
- Advanced Search : The “Advanced Search” function enables searching using multiple field names with multiple conditions to find specific data. The “Search” function allows the user to look for a specific entry within the available data and presents results that match the search parameters.
- Show all listing records: This functions like a refresh icon, retrieving and displaying all records in the listing.
- Export: The “Export” feature allows users to export selected or all data in CSV or PDF format.
- Filter: The “Filter” function in the delivery variance master allows users to customize their view of variances based on specific criteria.
Delivery Variance Master – Recording & Update:
- Users will be able to edit and update the delivery variances details as shown in below screen.
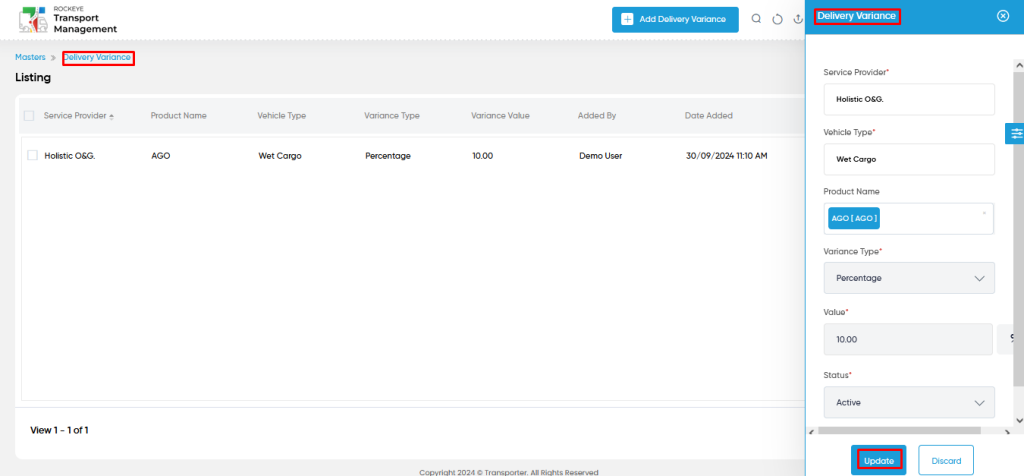
Users can perform the following actions:
- Save: The “Save” function allows the user to submit the required information while creating a new delivery variance.
- Discard: The “Discard” function allows the user to cancel the submission of information provided at the time of creating a new delivery variance.