Solution Overview
The Contract Management System (CMS) in the ERP ecosystem plays a vital role in streamlining the lifecycle of business contracts—from initiation and drafting, through internal reviews and external negotiations, all the way to final approval and execution. This digital workflow ensures compliance, version control, accountability, and efficient collaboration between internal teams and external counterparties.
The CMS empowers teams like the Business Unit, Legal, and Approval Authority to work in a structured and traceable way. Contracts can be created from predefined templates or uploaded manually, reviewed through internal workflows, and routed for digital signature. Once both parties approve, contracts are tracked throughout their active lifecycle with statuses like “In Use” and “Expired”. Notifications and conditions can also be configured for key events like renewals, expirations, or milestones.
The objective of CMS is to reduce risk, ensure policy compliance, and speed up contract turnaround time. It has a profound impact on operations by reducing delays, eliminating manual tracking, and providing full audit trails for every action and approval. It also ensures every stakeholder knows their responsibility and status at each phase.
Key Modules / Core Entities
- Company
Represents your organization. Contracts are owned and initiated from this entity, and approvals are routed based on company-level policies. - Counterparty (Customer/Vendor)
The external party involved in the contract. They can accept, reject, or comment on contract terms and sign digitally. - Contract Category
Categorizes contracts by types (e.g., NDA, MSA, Sales Agreement). Helps in selecting relevant templates and setting workflow rules. - Item Master
Captures goods/services associated with the contract, including pricing, units, and descriptions—especially for procurement- or sales-related contracts. - Variable Preset
Reusable fields or placeholders (e.g., dates, payment terms, delivery milestones) embedded into contract templates for dynamic generation. - Contract Templates
Pre-approved legal formats which users can select or upload. Ensures legal consistency and reduces drafting time. - Contracts
The central object that holds all contract information—template used, associated parties, versioning, attachments, status, comments, and history. - Signature Flow
Manages the approval and signature process—who signs, in what order, and tracks the status (Requested, Received, In Use, Expired).
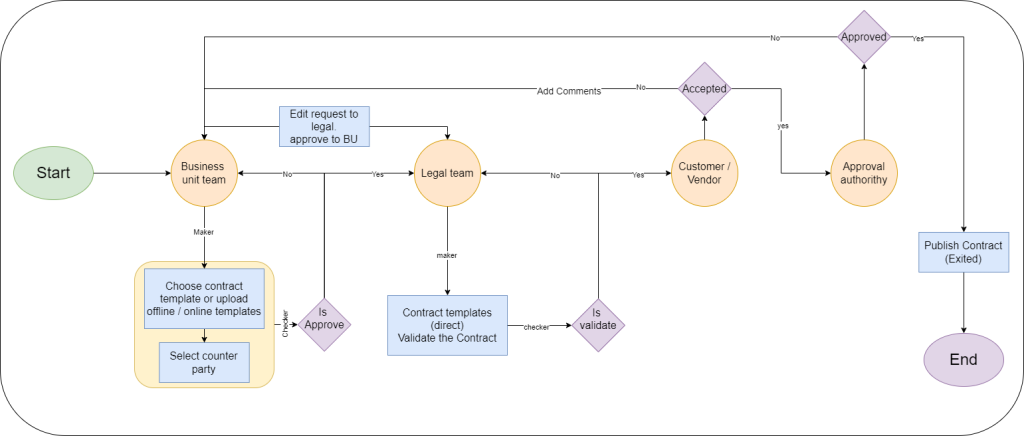
Entity Module Diagram Purpose & Flow
The Entity Module Diagram outlines the sequence of actions and responsibilities across all involved users:
- Start: Initiated by the Business Unit team (Maker).
- Template Selection & Counterparty Selection: Templates are either chosen from system-defined categories or uploaded offline.
- Internal Approval: Legal team validates the contract (can edit or request rework). If not validated, sent back to BU team.
- Counterparty Interaction: Once legally cleared, the contract is sent to the external party for acceptance, rejection, or comments.
- Final Approval: Approval Authority gives the final nod before contract publication.
- Contract Published: Status updated to “In Use” or marked as expired based on lifecycle events.